

Next: Biographical Sketches
Up: Collaborative Mathematics Environments
Previous: Vavasis
References
- 1
-
M. Aagaard and M. Leeser.
A framework for specifying and designing pipelines.
Technical Report TR EE--CEG--93--5, Cornell University, School of
Electrical Engineering, June 1993.
To appear in ICCD '93.
- 2
-
M. Aagaard and M. Leeser.
Verifying a logic synthesis tool in Nuprl.
In G. von Bochmann and D. K. Probst, editors, Computer Aided
Verification: Fourth International Workshop, volume 663 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 72--83, Berlin, June 1993. Springer-Verlag.
- 3
-
W. Aitken, R. L. Constable, and J. Underwood.
Using reflected decision procedures.
Tr, Dept. of Computer Science, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, 1993.
- 4
-
S. Allen, R. L. Constable, D. Howe, and W. Aitken.
The semantics of reflected proof.
In Proceedings of the Fifth Symposium on Logic in Computer
Science, pages 95--197. IEEE, June 1990.
- 5
-
J. M. Anderson. and M. S. Lam.
Global optimizations for parallelism and locality on scalable
parallel machines.
In SIGPLAN 93 Conference on Programming Language Design and
Implementation, pages 112--125. ACM Press, June 1993.
- 6
-
U. Banerjee.
Unimodular transformations of double loops.
In Proceedins of the Third Workshop on Languages and Compilers
for Parallel Computing, pages 192--219, Irvine, California, August, 1--3
1990.
Pitman Publishers.
- 7
-
R. Barrett, M. Berry, T. F. Chan, J. Demmel, J. Donato, J. Dongarra,
V. Eijkhout, R. Pozo, C. Romine, and H. V. der Vorst.
Templates for the Solution of Linear Systems: Building Blocks
for Iterative Methods.
SIAM, 1993.
- 8
-
D. Basin and R. L. Constable.
Metalogical Frameworks, chapter 1, pages 1--29.
Cambridge University Press, Great Britain, 1993.
- 9
-
D. Bau, I. Kodukula, V. Kotlyar, K. Pingali, and P. Stodghil.
Solving alignment using simple linear algebra.
In K. Pingali, U. Banerjee, D. Gelernter, A. Nicolau, and D. Padua,
editors, Languages and Compilers for Parallel Computing. Seventh
International Workshop., Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer-Verlag,
1994.
- 10
-
M. Beck, R. Johnson, and K. Pingali.
From control flow to dataflow.
Journal of Parallel Distributed Computing, 12:118--129, 1991.
- 11
-
F. Berger, V. Goldman, M. van Heerwaarden, and J. van Hulzen.
Automatic generation of numerical code for Jacobians and Hessians.
In P. Gaffney and E. Houstis, editors, Programming Environments
for High-Level Scientific Problem Solving, pages 309--320, Amsterdam, 1992.
North-Holland.
- 12
-
R. H. Berman.
Fourier transform algorithms for spectral analysis derived with
Macsyma.
In R. Pavelle, editor, Applications of Computer Algebra, pages
74--94. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, 1985.
- 13
-
T. Berners-Lee, R. Cailliau, J.-F. Groff, and B. Pollermann.
World-wide web: The information universe.
Electronic Networking: Research, Applications and Policy,
2(1):52--58, 1992.
- 14
-
T. Berners-Lee, R. Cailliau, A. Luotonen, H. F. Nielsen, and A. Secret.
The world-wide web.
Communications of the ACM, 37(8):76--82, August 1994.
- 15
-
R. F. Boisvert.
The architecture of an intelligent virtual mathematical software
repository system.
Mathematics and Computer Simulation, 1994.
in press.
- 16
-
D. M. Bond and S. A. Vavasis.
Multigrid for mixed boundary integral equations.
In Proc. 1992 Copper Mountain Conference on Iterative Methods,
1992.
- 17
-
W. Borst, V. Goldman, and J. van Hulzen.
GENTRAN90: A REDUCE package for the generation of FORTRAN 90
code.
In J. von zur Gathen and M. Giesbrecht, editors, Proceedings
ISSAC '94, New York, 1994 (to appear). ACM Press.
- 18
-
D. Callahan, K. Cooper, R. T. Hood, K. Kennedy, and L. M. Torczon.
Parascope: A parallel programming environment.
Technical Report Rice COMP TR88--77, Dept. of Computer Science, Rice
University, September 1988.
- 19
-
R. Chapman, G. Brown, and M. Leeser.
Verified high-level synthesis in bedroc.
In EDAC 92 --- The European Conference on Design Automation,
pages 59--63, March 1992.
- 20
-
S. Chatterjee, J. R. Gilbert, R. Schreiber, and S.-H. Teng.
Optimal evaluation of array expressions on massively parallel
machines.
Technical Report CSL--92--11, XEROX PARC, December 1992.
- 21
-
S. Chatterjee, J. R. Gilbert, R. Schreiber, and S.-H. Teng.
Automatic array alignment in data-parallel programs.
Technical Report CSL--92--13, XEROX PARC, April 1993.
- 22
-
J. Chirimar and D. J. Howe.
Implementing constructive real analysis: a preliminary report.
In J. J. P. Myers and M. J. O'Donnel, editors, Constructivity in
Computer Science: Summer Symposium, volume 613 of Lecture Notes in
Computer Science. Springer-Verlag, 1991.
- 23
-
A. Church.
A formulation of the simple theory of types.
The Journal of Symbolic Logic, 5:55--68, 1940.
- 24
-
E. Clarke and X. Zhao.
Analytica---an experiment in combining theorem proving and symbolic
computation.
In D. Kapur, editor, Automated Deduction --- CADE--11, volume
607 of Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, pages 761--765.
Springer-Verlag, New York, 1992.
- 25
-
R. Constable.
Constructive mathematics as a programming logic I: some principles
of theory.
In Annals of Mathematics, Vol. 24. Elsevier Science Publishers,
B.V. (North-Holland), 1985.
Reprinted from Topics in the Theory of Computation, Selected
Papers of the Intl. Conf. on ``Foundations of Computation Theory,'' FCT '83.
- 26
-
R. L. Constable, S. F. Allen, H. M. Bromley, W. R. Cleaveland, J. F. Cremer,
R. W. Harper, D. J. Howe, T. B. Knoblock, N. P. Mendler, P. Panangaden, J. T.
Sasaki, and S. F. Smith.
Implementing Mathematics with the Nuprl Proof Development
System.
Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1986.
- 27
-
R. L. Constable and C. Murthy.
Finding computational content from classical proofs.
In G. Huet and G. Plotkin, editors, Logical Frameworks, pages
341--362. Cambridge University Press, 1991.
- 28
-
R. L. Constable and M. J. O'Donnell.
A Programming Logic: With an introduction to the PL/CV
Verifier.
Winthrop Publishers, Cambridge, MA, 1978.
- 29
-
D. E. Culler, A. Dusseau, S. C. Goldstein, A. Krishnamurthy, S. Lumeta, T. von
Eicken, and K. Yellick.
Parallel programming in split-C.
In Proceedings of Supercomputing '93, Portland, Oregon,
November 1993. IEEE Computer Society Press.
- 30
-
R. Cytron, J. Ferrante, B. K. Rosen, M. N. Wegman, and F. K. Zadeck.
Efficiently computing static single assignment form and the control
dependence graph.
ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems,
13(4):451--490, October 1991.
- 31
-
R. G. Cytron, J. Ferrante, and V. Sarkar.
Compact representations for control dependence.
In Proceedings of the SIGPLAN 90 Conference on Programming
Language Design and Implementation, pages 337--351, White Plains, New York,
June 20--22 1990.
Published as ACm SIGPLAN Notices 25(6).
- 32
-
J. H. Davenport and B. M. Trager.
Scratchpad's view of algebra I: Basic commutative algebra.
Technical Report 90--31, School of Mathematical Sciences, University
of Bath, Bath, England, January 1990.
- 33
-
N. G. de Bruijn.
The mathematical language Automath, its usage and some of its
extensions.
In Symposium on Automatic Demonstration, volume 125 of
Lecture Notes in Mathematics, pages 29--61, Berlin, New York, 1970.
Springer-Verlag.
- 34
-
N. G. de Bruijn.
Automath; A Language for Mathematics, volume 52 of
Séminar de Mathématiques supérieures.
Les Presses de l'Université de Montréal, Montréal, 1973.
- 35
-
J. J. Dongarra and E. Grosse.
Distribution of mathematical software via electronic mail.
Communications of the ACM, 30:403--407, 1987.
- 36
-
S. Efremidis.
On Program Transformations.
PhD thesis, Cornell University, Dept. of Computer Science, Ithaca,
NY, June 1994.
- 37
-
S. Efremidis and D. Gries.
An algorithm for processing program transformations.
TR 93--1389, Cornell University, Dept. of Computer Science, Ithaca,
NY, October 1994.
- 38
-
J. Ferrante, K. J. Ottenstein, and J. D. Warren.
The program dependency graph and its uses in optimization.
ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems,
9(3):319--349, June 1987.
- 39
-
M. B. Forester.
Formalizing constructive real analysis.
TR 93--1382, Computer Science Dept., Cornell University, Ithaca, NY,
1993.
- 40
-
FORTRAN extended.
Technical Report ANSI Standard X3.198--1922, American National
Standards Institute, New York, 1992.
- 41
-
E. Gallopoulos, E. Houstis, and J. R. Rice.
Future resarch directions in problem solving environments for
computational science.
CSRD Report No. 1259, Center for Supercomputing Research and
Development, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, West Lafayette,
Illinois, October 1992.
- 42
-
A. George and J. W. H. Liu.
Computer solution of large sparse positive definite systems.
Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J., 1981.
- 43
-
J. R. Gilbert, C. Moler, and R. Schreiber.
Sparse matrices in MATLAB: design and implementation.
Technical Report 91--4, Xerox Palo Alto Research Center, 1991.
- 44
-
G. H. Golub and C. F. Van Loan.
Matrix Computations.
Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, 1989.
- 45
-
M. J. C. Gordon.
Hol: A proof generating system for higher-order logic.
In G. Britwistle and P. Subrahmanyam, editors, VLSI
Specification, Verification and Synthesis, pages 73--128. Kluwer, 1988.
- 46
-
J. Grant O. Cook and J. F. Painter.
ALPAL: A tool to generate simulation codes from natural
descriptions.
In E. N. Houstis, J. R. Rice, and R. Vichnevetsky, editors,
Expert Systems for Scientific Computing, pages 401--419. Elsevier Science
Publishers, Amsterdam, 1992.
- 47
-
D. Gries and D. Volpano.
The transform---a new language construct.
Structured Programming, 11:1--10, 1991.
- 48
-
E. Hairer, S. P. Nørsett, and G. Wanner.
Solving Ordinary Differential Equations: Non-Stiff Problems,
volume 1.
Springer-Verlag, New York, 1987.
- 49
-
E. Hairer, S. P. Nørsett, and G. Wanner.
Solving Ordinary Differential Equations: Stiff Problems,
volume 2.
Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991.
- 50
-
M. D. Hirsch, C. H. Papadimitriou, and S. A. Vavasis.
Exponential lower bounds for finding Brouwer fixed points.
Journal of Complexity, 5:379--416, 1989.
- 51
-
G. Huet and G. P. (eds.).
Logical Frameworks.
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England, 1991.
- 52
-
R. Huff.
Lifetime sensitive modulo searching.
In SIGPLAN 93 Conference on Programming Language Design and
Implementation, pages 258--267. ACM Press, June 1993.
- 53
-
P. B. Jackson.
Exploring abstract algebra in constructive type theory.
In A. Bundy, editor, Automatic Deduction --- CADE--12, volume
814 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 590--604, New York,
June 1994. Springer-Verlag.
- 54
-
P. B. Jackson.
Enhancing the Nuprl Proof Development System and Applying it
to Computational Abstract Algebra.
PhD thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, January 1995.
- 55
-
R. Jagadeesan, P. Panaganden, and K. Pingali.
A fully abstract semantics for a first-order functional language with
logic variables.
ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems,
13(4):577--625, October 1991.
- 56
-
R. Jagadeesan and K. Pingali.
From control flow to dataflow.
In Proceedings of the 19th Annual ACm Symposium on Programming
Languages (POPL19), January 1992.
- 57
-
R. D. Jenks and R. S. Sutor.
AXIOM: The Scientific Computation System.
Springer-Verlag, New York and NAG, Ltd. Oxford, 1992.
- 58
-
R. Johnson, D. Pearson, and K. Pingali.
The program structure tree: Computing control regions in linear time.
In Proceedings of the SIGPLAN 94 Conference on Programming
Language Design and Implementation, pages 171--185, Orlando, Florida, June
1994.
- 59
-
R. Johnson and K. Pingali.
Dependence-based program analysis.
In Proceedings of the SIGPLAN 93 Conference on Programming
Language Design and Implementation, pages 78--89, Alburquerque, New Mexico,
June 1993.
- 60
-
V. Kahan.
The interface between symbolic and numeric computation.
Notes and slides presented at IBM Europe Institute on Symbolic
Mathematical Computation, Oberlech, Austria, July 1991.
- 61
-
D. Kahaner, C. Moler, and S. Nash.
Numerical Methods and Software.
Prentice Hall, Englewod Cliffs, NJ, 1989.
- 62
-
E. Kant.
An environment for synthesizing mathematical modeling programs.
In Proceedings of Working Conference on Programming Environments
for High-Level Scientific Problem Solving. IFIP, 1991.
- 63
-
E. Kant.
Synthesis of mathematical modeling software.
IEEE Software, 5, 1993.
- 64
-
M. Leeser, R. Chapman, M. Aagaard, M. Linderman, and S. Meier.
High level synthesis and generating fpgas with the bedroc system.
Journal of VLSI Signal Processing, 6:191--214, 1993.
- 65
-
W. Li and K. Pingali.
Access normalization: Loop restructuring for NUMA compilers.
In Fifth Architectural Support for Programming Languages and
Operating Systems, pages 285--295. ACM Press, 1992.
- 66
-
W. Li and K. Pingali.
Access Normalization: Loop restructuring for NUMA compilers.
ACM Transactions on Computer Systems, 11(4):353--375, November
1993.
- 67
-
W. Li and K. Pingali.
A singular approach to loop transformations based on non-singular
matrices.
In e. a. Uptal Bannerjee, editor, Langauges and Compilers for
Parallel Computing: 5th International Workshop, number 757 in Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 391--405, Berlin, 1993. Springer-Verlag.
- 68
-
W. Li and K. Pingali.
A singular approach to loop transformations based on non-singular
matrices.
International Journal on Parallel Processing, 22(2):183--205,
April 1994.
- 69
-
R. Liska and L. Drska.
FIDE: A REDUCE package for automation of FInite difference
method for solving pDE.
In S. Watanabe and M. Nagata, editors, ISSAC '90: Proceeedings
of the International Symposium on Symbolic and Algebraic Computation, pages
169--176. ACM, Addison-Wesley, 1990.
- 70
-
R. Liska, M. Y. Shashkov, and A. V. Solovjov.
Support-operators method for PDE discretization: Symbolic
algorithms and realization.
In Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, pages 173--183.
IMACS, 1993.
- 71
-
R. Liska and S. Steinberg.
Applying quantifier elimination to stability analysis of difference
schemes.
The Computer Journal, 36(5):497--503, 1993.
- 72
-
J. W. H. Liu.
The multifrontal method for sparse matrix solution: Theory and
practice.
SIAM Review, 34(1):82--109, March 1992.
- 73
-
Y. A. Liu and T. Teitelbaum.
Systematic derivation of incremental programs.
TR 94--1444, Cornell University, Dept. of Computer Science, Ithaca,
NY, August 1994.
- 74
-
R. Loos.
Toward a formal implementation of computer algebra.
In Proceedings of EUROSAM '74, volume 8, pages 9--16. ACM,
August 1974.
- 75
-
M. Lowry, A. Philpot, T. Pressburger, and I. Underwood.
Amphion: Automatic programming for scientific subroutine libraries.
In 8th International Symposium on Methodologies for Intelligent
Systems, 1994.
- 76
-
P. Martin-Löf.
Constructive mathematics and computer programming.
In Sixth International Congress for Logic, Methodology, and
Philosophy of Science, pages 153--75. North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1982.
- 77
-
Matlab Reference Guide.
The MathWorks, Inc., Cochituate Place, 24 Prime Park Way, Natick, MA
01760, 1992.
- 78
-
D. A. McAllester.
ONTIC: A Knowledge Representation System for Mathematics.
MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1989.
- 79
-
G. L. Miller, S.-H. Teng, W. Thurston, and S. A. Vavasis.
Automatic mesh partitioning.
In A. George, J. R. Gilbert, and J. W. H. Liu, editors, Graph
Theory and Sparse Matrix Computation, volume 56 of IMA Volumes in
Mathematics and its Applications. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1993.
- 80
-
G. L. Miller, S.-H. Teng, and S. A. Vavasis.
A unified geometric approach to graph separators.
In Proceedings of the Symposium on Foundations of Computer
Science, pages 538--547, 1991.
- 81
-
G. L. Miller and S. A. Vavasis.
Density graphs and separators.
In Proceedings of the SIAM-ACM Symposium on Discrete
Algorithms, 1991.
- 82
-
S. A. Mitchell and S. A. Vavasis.
Quality mesh generation in three dimensions.
In Proceedings of the ACM Computational Geometry Conference,
pages 212--221, 1992.
Also appeared as Cornell C.S. TR 92--1267.
- 83
-
J. J. Moré and S. A. Vavasis.
On the solution of concave knapsack problems.
Mathematical Programming, 49:397--411, 1991.
- 84
-
M. Moudgill, K. Pingali, and S. Vassiliadis.
Register renaming and dynamic speculation: an alternative approach.
In Proceedings of the 26th International Symposium on
Microarchitecture (MICRO 26), pages 202--213, Austin, TX, December 1993.
- 85
-
C. Murthy.
Extracting Constructive Content for Classical Proofs.
PhD thesis, Cornell University, Dept. of Computer Science, 1990.
(TR 89--1151).
- 86
-
J. K. Ousterhout.
Tcl and the Tk Toolkit.
Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1994.
- 87
-
S. Owre, J. M. Rushby, and N. Shankar.
PVS: A prototype verification system.
In D. Kapur, editor, Automated Deduction --- CADE--11, volume
607 of Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, pages 748--752,
Saratoga, NY, 1992. Springer-Verlag.
- 88
-
R. L. Peskin, S. S. Walther, and T. Boubez.
Computational steering in a distributed computer based user system.
In E. N. Houstis and J. R. Rice, editors, Artificial
Intelligence, Expert Systems and Symbolic Computing, pages 104--113.
Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, 1992.
- 89
-
K. Pingali and G. Bilardi.
APT: An optimal data structure for control dependence.
Technical Report to appear, Dept. of Computer Science, Cornell
University, Ithaca, NY 14853, November 1994.
- 90
-
N. Pitsianis and C. Van Loan.
Automatic implementation of optimized FFT codes.
in preparation, 1994.
- 91
-
C. D. Polychronopoulos, M. B. Gikar, M. R. Haghighat, C. L. Lee, B. P. Leung,
and D. A. Schouten.
The structure of Parafrase-2: An advanced parallelizing compiler
for C and FORTRAN.
In D. Gelernter, A. Nicolau, and D. Padua, editors, Languages
and Compilers for Parallel Computing, pages 423--453. Pitman Publishing,
1990.
- 92
-
A. Pothen, H. D. Simon, and K.-P. Liou.
Partitioning sparse matrices with eigenvectors of graphs.
SIAM Journal of Matrix Analysis and Applications, 11:430--452,
1990.
- 93
-
J. Purtilo.
The polylith software bus.
ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems,
16(1):151--174, January 1994.
- 94
-
J. Purtilo, R. T. Snodgrass, and A. L. Wolf.
Software bus organization: Reference model and comparison of two
existing systems.
MIFWG 8, University of Arizona Computer Science Department, 1991.
- 95
-
T. Reps and T. Teitelbaum.
The Synthesizer Generator Reference Manual.
Springer-Verlag, New York, third edition, 1988.
- 96
-
A. M. Rogers and K. Pingali.
Register renaming and dynamic speculation: an alternative approach.
IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems,
5(3):281--298, March 1994.
- 97
-
B. Russell.
Mathematical logic as based on a theory of types.
American Journal of Mathematics, 30:222--62, 1908.
- 98
-
F. Santosa and M. Vogelius.
A backprojection algorithm for electrical impedance imaging.
SIAM J. Applied Math, 50:216--245, 1990.
- 99
-
D. A. Schmidt.
The Structure of Typed Programming Languages.
Foundations of Computing. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1994.
- 100
-
D. S. Scott.
Constructive validity.
In Symposium on Automatic Demonstration, volume 125 of
Lecture Notes in Mathematics, pages 237--275, Berlin, New York, 1970.
Springer-Verlag.
- 101
-
D. S. Scott.
Data types as lattices.
SIAM Journal of Computing, 5:522--87, 1976.
- 102
-
D. S. Scott.
Teaching projective geometry via computer.
Mellon College of Science News, 8:1--7, 1990.
- 103
-
D. S. Scott.
Exploration with mathematica.
In R. Rashid, editor, Carnegie Mellon Computer Science: a 25th
Year Commemorative, chapter 22, pages 505--515. Addison-Wesley, 1991.
- 104
-
D. R. Smith.
KIDS: A semi-automated program development system.
IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 16(9):1024--1043,
September 1990.
- 105
-
V. Sreedhar and G. Gao.
Computing
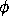 -nodes in linear time using DJ-graphs.
Technical Report ACAPS Memo 75, McGill University, January 1994.
-nodes in linear time using DJ-graphs.
Technical Report ACAPS Memo 75, McGill University, January 1994.
- 106
-
J. M. Stern and S. A. Vavasis.
Nested dissection for sparse nullspace bases.
SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 14:766--775,
1993.
- 107
-
M. Stickel, R. Waldinger, M. Lowry, T. Pressburger, and I. Underwood.
Deductive composition of astronomical software from subroutine
libraries.
In A. Bundy, editor, Lecture Notes in Computer Science 814,
Automatic Deduction --- CADE--12, pages 341--355, New York, 1994. Springer
Verlag.
- 108
-
T. Teitelbaum and T. Reps.
The Cornell Program Synthesizer: a syntax--directed programming
environment.
Communications of Association for Computing Machinery,
24(9):563--73, 1981.
- 109
-
S. Thompson.
Type Theory and Functional Programming.
Addison-Wesley, Wokingham, England, 1991.
- 110
-
R. Turner.
Logics for Artificial Intelligence.
Ellis Horwood Series in Artificial Intelligence. Halsted Press, New
York, 1984.
- 111
-
S. A. Vavasis.
Gaussian elimination with pivoting is P-complete.
SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics, 2:412--423, 1989.
- 112
-
S. A. Vavasis.
Quadratic programming is in NP.
Information Processing Letters, 36:73--77, 1990.
- 113
-
S. A. Vavasis.
Automatic domain partitioning in three dimensions.
SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing,
12:950--970, 1991.
- 114
-
S. A. Vavasis.
Nonlinear Optimization: Complexity Issues.
Oxford University Press, New York, 1991.
- 115
-
S. A. Vavasis.
Approximation algorithms for indefinite quadratic programming.
Mathematical Programming, 57:279--311, 1992.
- 116
-
S. A. Vavasis.
Local minima for indefinite quadratic knapsack problems.
Mathematical Programming, 54:127--153, 1992.
- 117
-
S. A. Vavasis.
Preconditioners for boundary integral equations.
SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 13:905--925,
1992.
- 118
-
S. A. Vavasis.
Black-box complexity of local minimization.
SIAM Journal on Optimization, 3:60--80, 1993.
- 119
-
S. A. Vavasis.
Stable finite elements for problems with wild coefficients.
Technical Report 93--1364, Department of Computer Science, Cornell
University, Ithaca, NY, 1993.
To appear in SIAM J. Numerical Analysis.
- 120
-
S. A. Vavasis.
Stable numerical algorithms for equilibrium systems.
SIAM Journal of Matrix Analysis and Applications,
15:1108--1131, 1994.
- 121
-
S. A. Vavasis and Y. Ye.
An accelerated interior point method whose running time depends only
on A.
Technical Report 93-1391, Department of Computer Science, Cornell
University, Ithaca, NY, 1993.
Submitted to Math. Progr.
- 122
-
P. S.-H. Wang.
FINGER: A symbolic system for automatic generation of numerical
programs in finite element analysis.
Journal of Symbolic Computing, 2:305--316, 1986.
- 123
-
S. Weerawarana, E. N. Houstis, and J. R. Rice.
An interactive symbolic-numeric interface for parallel ELLPACK for
building general PDE solvers.
In B. Donald, D. Kapur, and J. Mundy, editors, Symbolic and
Numerical Computation in Artificial Intelligence. Academic Press, 1992.
- 124
-
M. Wolf and M. S. Lam.
A data locality optimizing algorithm.
In ACM SIGPLAN 91 Conference on Programming Language Design and
Implementation, pages 30--44, June 1991.
- 125
-
M. Wolf and M. S. Lam.
A loop transformation theory and an algorithm to maximize
parallelism.
IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, October
1991.
- 126
-
H. Zima and B. Chapman.
Supercompilers for Parallel and Vector Computers.
ACM Press, New York, NY, 1991.
- 127
-
R. Zippel.
A constraint based scientific programming language.
In V. Saraswat and P. V. Hentenryck, editors, Principles and
Practice of Constraint Programming: The Newport Papers, pages 115--130. MIT
Press, Cambridge, MA, 1995.
- 128
-
R. E. Zippel.
The Weyl computer algebra substrate.
In Design and Implementation of Symbolic Computation Systems
'93, volume 722 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 303--318,
New York, 1993. Springer-Verlag.
nuprl project
Tue Nov 21 08:50:14 EST 1995